25.06.2021
On 1 July 2021, EU member states must introduce important changes to their legislation in the taxation of the supplies of goods and services that are generally contracted online by end consumers (B2C) and sent or rendered by businesses from another member state or third countries.
Every operator involved in the e-commerce supply chain is affected, from online sellers and platforms established both in or outside the EU, to couriers, customs brokers and administrations, with consumers and the consumer experience also being impacted.
These developments mean that B2C e-commerce transactions will be subject to VAT at the destination, that is, in the member state of the arrival of the goods or the member state in which the consumer is resident. The rules are aimed at overcoming the administrative barriers resulting from multiple registrations and the effects of market distortion, by doing the following:
- increasing tax revenues for member states, reducing collection losses and tackling cross-border trade fraud
- guaranteeing the impartiality of consumer purchasing decisions, thereby protecting competition between EU and non-EU suppliers
- simplifying the existing rules by reducing administrative burdens and VAT management costs for operators
The VAT management related to e-commerce transactions will be based on the expansion of the One-Stop Shop (OSS), which is to become the general procedure for managing and collecting VAT on e-commerce transactions at an EU level. Likewise, electronic interfaces that facilitate e-commerce (i.e., platforms/marketplaces) will be required to assist in the collection, management and control of VAT.
Overview of changes
The key changes can be summarized as follows:
- The existing thresholds for distance sales of goods within the EU will be replaced by a new EU threshold of EUR 10,000. Below this threshold, distance sales of goods within the EU may remain subject to VAT in the member state where the taxable person is established.
- A new category of supply of goods is created: distance sales of imported goods in consignments not exceeding EUR 150.
- Imports of small consignments of up to EUR 22 will no longer be VAT-exempt. This means that all goods imported into the EU will be subject to the EU VAT regime.
New VAT compliance measures are being implemented to facilitate reporting for operators: online sellers can register in one EU member state to declare and pay VAT on all distance sales of goods and cross-border supplies of services to customers within the EU through the new OSS. In addition, a new special scheme covering the import of goods subject to a distance sales transaction and in consignments not exceeding EUR 150 has been created to simplify declaring and paying VAT, namely the Import One-Stop Shop (IOSS).
- For postal and courier companies that facilitate the payment of import VAT when the goods are supplied from outside the EU, new simplification measures will be introduced for distance sales of imported goods in consignments not exceeding EUR 150 where the IOSS is not used (special arrangements).
- Under certain circumstances, online platforms that facilitate the e-commerce transaction are deemed to have received and supplied the goods themselves for VAT purposes (“deemed supplier”). This is regardless of whether they have any legal title over the goods. New record-keeping requirements are introduced for such operators.
- Certain invoice obligations have been amended as a result of the above-mentioned changes.
Distance sales
Currently, cross-border distance selling of goods to consumers within the EU is taxable in the destination country only if a certain threshold[1] is exceeded and the seller is responsible for, or otherwise facilitates, the transport. This may also be the case where the supplier opts for VAT taxation in the destination country. Otherwise, said supply is taxable at origin.
As of 1 July 2021, the referred thresholds will not be applicable. A uniform threshold of EUR 10,000 will enter into force. Therefore, the supplier will charge VAT where the goods are located if the total turnover of the intra-community amount of the distance sales and certain services provided to individuals does not exceed EUR 10,000 in a fiscal year. The new distance sales regime still allows taxpayer to opt to charge VAT at the destination member state.
The transport of the goods and the involvement of the supplier (direct or indirect) are key for distance selling rules. The supplier would be considered as being involved in the transport:
(a) if the dispatch or transport of the goods is subcontracted by the supplier to a third party who delivers the goods to the customer
(b) if the dispatch or transport of the goods is provided by a third party but the supplier bears responsibility for the delivery
(c) where the supplier invoices and collects the transport fees from the customer and remits them to a third party that will arrange the dispatch or transport of the goods
(d) where the supplier promotes by any means the delivery services of a third party to the customer, puts the customer and a third party in contact or otherwise provides to a third party the information needed for the delivery of the goods to the customer
These changes ensure that VAT remains payable in the destination member state even where a separate entity provides shipment to the customer.
However, goods will not be considered to have been dispatched or transported by or on behalf of the supplier where:
(a) the customer transports the goods themselves
(b) the customer arranges the delivery of the goods with a third person and the supplier does not intervene directly or indirectly to provide or help organize the dispatch or transport of those goods
New OSS and IOSS
The existing Mini One-Stop Shop (MOSS) [2] regime is being extended as of 1 July 2021 for all services provided to customers and distance sales of goods. The new OSS regime will allow businesses to use a single point of contact for their VAT compliance obligations, enabling them to do the following:
- register for VAT online in one member state for all intra-EU distance sales of goods and for B2C supplies of services and thus avoid VAT registration in multiple member states
- declare and pay VAT due on all these supplies of goods and services in a single online quarterly return
- work with the tax administration of their own member state and in their own language, even for cross-border transactions
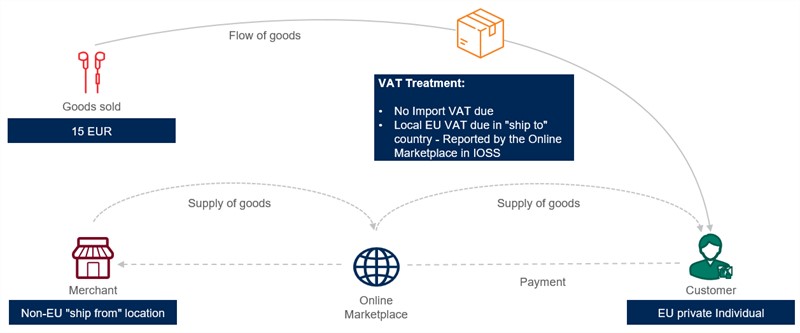
In addition, the IOSS facilitates the collection, declaration and payment of VAT for suppliers and electronic interfaces carrying out distance sales of imported goods to buyers in the EU. If the IOSS is used, the goods are exempt from import VAT, with the supplier being required to pay local VAT on the sale to the customer.
Non-EU sellers or non-EU electronic interfaces facilitating e-commerce supplies that want to use the IOSS scheme must appoint an intermediary established in the EU.[3] This new regime can only be used when the value of the imported goods does not exceed EUR 150 and cannot be applied to excise goods of any value. In order to grant the import VAT exemption, the corresponding IOSS number must be communicated to customs authorities.
Distance sales of imported goods
The new e-commerce rules provide for a new definition of imported goods transported from non-EU territories to EU customers. This new type of supply will apply if both the following conditions are met:
- the transaction is considered a B2C supply
- the goods supplied are neither a new means of transport nor goods supplied after assembly or installation, with or without a trial run, by, or on behalf of, the supplier
The place of taxation depends on whether the supply takes place within the same member state of importation and whether the new IOSS regime is applicable to the transaction.
If the member state of importation is the same as the member state of the arrival of the goods, the following scenarios are possible:
- IOSS regime applies: Distance sales of imported goods are VAT-taxable in the member state where the transport of goods to the customer ends (i.e., member state of importation). The import is VAT-exempt.
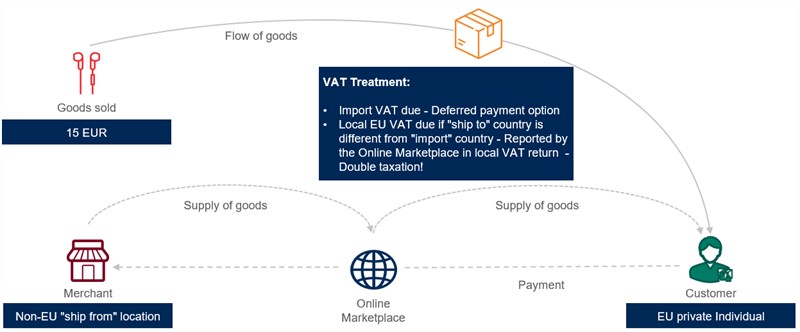
- IOSS regime does not apply: The place of supply should be determined according to the regular non-distance sales rules, i.e., the supplier will only be required to charge VAT in the member state of destination if it acts as the importer of record. The import is subject to import VAT. Note that the IOSS regime is not obligatory, and if the supplier does not apply it then the special arrangements for the collection of import VAT referred to below will apply.
If the member state of importation is different from the member state of destination of the goods, the following scenarios are possible:
- The supply of goods is considered distance sales of imported goods of low-value[4] and the supplier has opted for IOSS. Distance sales of imported goods are VAT taxable in the member state where the transport of goods to the customer ends. The preceding import is VAT-exempt.
- The supply of goods is not considered distance sales of imported goods of low value. The supply will be subject to import VAT in the member state of importation. This import will be followed by a deemed supply of goods from the former member state and taxable in the member state where the transport of goods to the customer ultimately ends. Under existing import VAT recovery restrictions, where the supplier is not listed as an importer it may be unable to recover the import VAT paid, leading to double taxation.
New EU VAT rules for imported e-commerce purchases of less than EUR 150 with IOSS
New EU VAT rules for imported e-commerce purchases of less than EUR 150 without IOSS
Elimination of exemption related to imports of small consignments
The current VAT exemption of low-value consignments imports (i.e., the value of which is up to EUR 22) will be removed. Therefore, all goods imported into the EU will now be subject to import VAT.
Special arrangement on import VAT
A new special arrangement has been introduced for the declaration and payment of import VAT for low-value goods supplied to a customer in the member state of importation, where neither the IOSS scheme nor the standard VAT collection mechanism on imports are used. This regime applies for goods not exceeding EUR 150 in value and only applies to goods that are not subject to excise duties. The simplification measure will allow customs declarants (e.g., postal operators and couriers) to remit VAT collected on a monthly basis.
Electronic interfaces that facilitate e-commerce
An electronic interface (EI) may be a website, portal, gateway, marketplace, platform, application program interface, etc. It should be understood as a broad concept.
The term “facilitates” means the use of an electronic interface to allow a customer and a supplier offering services or goods for sale through the electronic interface to enter into a contact that results in a supply of goods or services through that electronic interface.
EIs will have the following new roles for VAT purposes in the EU:
- They may be “deemed suppliers” for the underlying goods, meaning that they are treated as though they purchase the goods from the legal supplier and supplied the goods in their own name to the customer.
- They will have certain record-keeping obligations.
EIs will be considered a “deemed supplier” if they facilitate the following:
- distance sales of goods imported into the EU of a value not exceeding EUR 150
- supplies of goods to customers in the EU irrespective of their value, when the underlying supplier/seller is not established in the EU
However, they will not become a “deemed supplier” in the following transactions:
- goods in consignments of a value exceeding EUR 150 imported into the EU, irrespective of where the actual supplier/seller is established
- goods that are located in the EU at the time of sale, irrespective of their value, if the underlying supplier/seller is established in the EU
In order to declare and pay VAT due in other member states, EIs will be able to register for the OSS and IOSS. Both OSS and IOSS are open for registration from 1 April 2021 and will be ready to use from 1 July 2021.
As a result, for VAT purposes, an EI is treated as if it is the actual supplier of the goods and will be liable to account for VAT on these sales. The EI facilitating the sale is deemed, therefore, to have received and supplied the goods.
In addition, EIs will need to keep records for the transactions they facilitate, irrespective of whether they become “deemed suppliers.” Such records should be kept for 10 years after the end of the fiscal year in which the transaction took place. Records must be made available to member states upon request.
Invoicing obligations
The rules applicable to date on e-commerce transactions mean that invoices should be issued according to the legislation of the EU member state in which the transaction is deemed to take place.
After 1 July 2021, that rule changes with respect to businesses applying the OSS. These businesses should issue sales invoices according to their country of identification (i.e., the member state in which they are registered for the OSS). The VAT Directive does not impose a mandatory invoicing obligation for such supplies to consumers within the EU. Nonetheless, member states may set forth the requirement to issue an invoice for such supplies in their national legislation.
In connection with sales facilitated via an EI, the invoicing regulations could be more complicated. Below is a table summarizing the different invoicing obligations:[5]
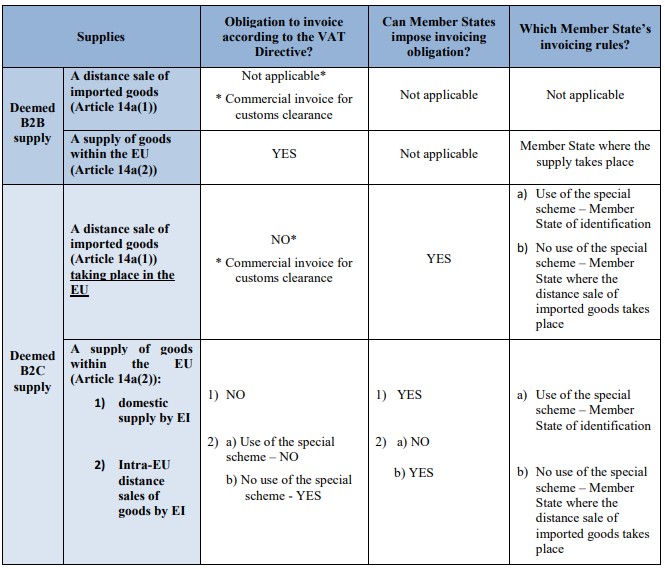
_________________
[1] These thresholds are not applicable for excise goods.
[2] MOSS currently applies for ESS, telecoms and broadcasting services: Union and non-Union scheme.
[3] However, that obligation should not apply if the non-EU entity is established in a country with which the EU has concluded an agreement on mutual assistance.
[4] As from 1 July 2021, the VAT threshold of EUR 10 or EUR 22 will be abolished. There will be a threshold of EUR 150. Importation may continue to be exempt from VAT for goods not exceeding EUR 150 subject to the IOSS regime.
[5] Taken from EU Commission Explanatory Notes on VAT e-commerce rules.



